



Citi Private Bank
Serving worldly, wealthy individuals and families.






GLOBAL PRIVATE BANKING
Customized private banking that crosses borders. Sophisticated financial services to preserve and grow wealth worldwide.


Serving the world for over 200 years
Providing global banking services that enable clients to flourish and grow on their journey from ambition to achievement since 1812.

1812
City Bank of New York is founded

1820
Our journey in trust and estate planning begins

1865
City Bank becomes National City Bank of New York

1897
Our organization enters the foreign exchange business

1915
National City Bank gains a foothold in Europe

1935
Citi Investment Management starts managing portfolios

1960
Citi Trust's first overseas trust company is born

1971
Our Law Firm Group is founded

1979
Citi’s Art Advisory & Finance business is born

1986
The Private Banking Group is established

1998
Citicorp announces $140bn merger with Travelers Group
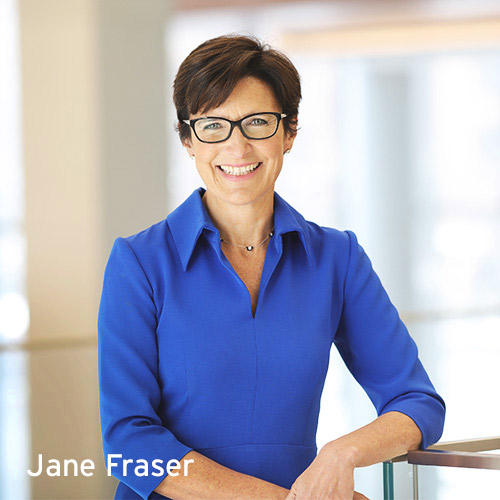

2009
The Private Bank appoints its first female CEO

2021
The Private Bank joins forces with Citi Global Wealth

Today
We serve clients from 60 offices globally






One global team
Working closely with Citi’s Institutional Clients Group, Citi Private Bank offers access to the world’s most sophisticated services for wealth.




Our unique community
The events and introductions we provide create vital connections between clients of the Private Bank.
Global citizens
We serve inspirational individuals and families who make an outstanding contribution to the world around us.